Upload Visual Studio 2019 project to GitHub. Upload Visual Studio 2019 project to GitHub. Use Git as the default version control experience in Visual Studio 2019 or Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) for centralized version control right out of the box. From the new Git menu, you can clone, create, or open your own repositories.
CodeStream is a developer collaboration platform that integrates all of your essential dev tools into Visual Studio. Eliminate context-switching and simplify code discussion and code review by putting collaboration tools in your IDE.
Integrations
- Code Hosts: Bitbucket, Bitbucket Server, GitHub, GitHub Enterprise, GitLab, GitLab Self-Managed
- Issue Trackers: Asana, Azure DevOps, Bitbucket, Clubhouse, GitHub, GitHub Enterprise, GitLab, GitLab Self-Managed, Jira, Linear, Trello, YouTrack
- Messaging Services: Slack, Microsoft Teams
Requirements
- CodeStream requires Visual Studio 2017 or later, and is also available for JetBrains, VS Code or Atom.
- Your repository must be managed by Git, or a Git hosting service like GitHub.
Create, review and merge GitHub pull requests and GitLab merge requests inside Visual Studio, with full source-tree and full file access, your favorite keybindings, built-in diff tool, and code intelligence.
CodeStream's lightweight feedback requests let you get feedback on your changes regardless of the current state of your repo, without the friction of committing, pushing or issuing a pull request. Your teammates can review your changes right in their IDE, with full file context, and with no need to set aside their current work to switch branches or pull the latest.
CodeStream’s feedback requests are so easy that you can start doing them throughout the development process instead of waiting until the end. You’re a few days into a sprint and have some work stubbed out? Maybe some work that hasn’t even been committed. Get feedback on your work-in-progress so that you can identify and resolve issues early instead of saving those gotchas for when you need to get the code merged.
Rather than copying & pasting, CodeStream enables in-editor commenting on any code in your repository, with optional sharing to Slack, MS Teams or via email, with automatic at-mentioning of code authors via git blame.
Your teammates can participate in the discussion right from their IDE, or from Slack, Teams, or replying to the email.
CodeStream turns conversation into documentation by capturing all of the discussion about your code, and saving it with your code. Comment and code review threads are automatically repositioned as your code changes, even across branches. All with zero effort on your part.
Previously discussed questions and issues that explain important decisions are now accessible right where you need them, when you need them. Just click on the codemark to expand it and see how something works or why something was done a certain way.
Where are messages stored?
Your team’s codemarks, which include the message text and the code snippet, are stored in the cloud on CodeStream’s servers. CodeStream uses best practices when it comes to security, but if your team has stringent infosec requirements we also offer an on-prem solution.
Check out the user guide for more information on getting started with CodeStream. Please follow @teamcodestream for product updates and to share feedback and questions. You can also email us at support@codestream.com.
Contents
- Doing It In Visual Studio 2019
- Common Operations
- Solving Common Problems
Note
Some of the information below may become outdated with the upcoming VS Git revamp, which you can read about here: Improved Git Experience in Visual Studio 2019 | Visual Studio Blog
What problem(s) does Git solve?
- Multi-user offline development
- Rapid, dependable branching and merging
- Decentralized version control
Git is a distributed version control system that was originally developed by Linus Torvalds in April 2005 to replace BitKeeper, which was withdrawn from free use due to alleged reverse engineering by SourcePuller creator Andrew Tridgell.
Torvalds needed a system that could manage the Linux kernel development and scale to hundreds of merges performed in seconds. Git has been maintained by Junio Hamano since July 2005.
Git is currently the most-used version control system by far. Microsoft recommends Git, has contributed to its development, and hosts the Windows source code using Git--the largest such repository in the world.
How does Git basically work?
A folder, .git, contains the complete repository for files and folders underneath it. A clone of a repository contains the same history as the original.
The repository is a file system. Each file is named with an SHA-1 hash. A file contains either the actual content of source code file, or contains a tree of hash file names. In this way, Git maintains references, sometimes called 'pointers'--the hash file names--to content.
There's a file that contains the reference to the root of the solution. From here, all the links to other files can be traced, so this becomes the current state.
If any file changes, Git creates a new copy of the file with a new hash reference, updates links to it, and creates a new root-level reference. This becomes the new point-in-time version.
Branches exist by creating a file with the branch name, e.g. 'master', whose content points to a particular root reference file. When people talk about branching in Git being 'cheap,' it's because, to branch from another branch, all Git has to do is create another file, e.g. 'feature-1,' with the same reference file name.
If Charlene clones a repository from Blake, all she's doing is making a copy of the .git folder. Let's say Charlene and Blake each make a change to the same file. Each of them will get a different new reference hash. This is how Git knows to merge files: when it finds a divergence in the tree, it can trace backward in the references to find the common ancestor, then determine the changes via a three-way comparison. Once the differences are resolved, a new version of the file is created with a new reference name.
The process is exactly the same with repositories located on remote servers. The only difference is that remote repositories are typically 'bare,' meaning there's no working folder.
Anyone can create a bare repository on their local file filesystem. It's really just the contents of the .git folder moved to the root level.
Remote branch reference information is maintained in a .git folder named remotes. Where the remotes are located is maintained in a .git config file.
What's important to understand at this point is that your repository can contain branches for your local work, and branches for remote work. When you fetch a remote branch, the contents are merged into your local copy of that branch, e.g. origin/master. You then decide whether to merge those files into your local branch, i.e. master
When it comes to tracking local changes, there are potentially three versions of the file in play at any one time.

First, there's the version of the file you're editing. This is the working file.
Second, there's the version of the file you're going to commit. This is the staged file. (Also called being in the 'index'.)
Third, there's the version of the file since the last commit. This is the repository file.
How does this look in practice? Let's say the last committed file named Test.txt has one line:
You edit the file and add a line:
So, now your working file is changed, but Git doesn't know about the changes. You add the file to the index via git add Test.txt.
If you were to commit now, the repository file would be updated to match the staged file. But what if you don't commit, and instead add a third line?

If you commit, Git will still only update the repository file with the two lines from the staged file. You'd have to git add again to stage the file with all three lines.
This is a very flexible approach, letting you commit only the changes that you want. While I don't cover it in this guide, it's even possible to only commit portions of a file, called 'hunks.'
What's a typical daily flow?
Let's assume you've already cloned a repository from a remote server, and have configured your local Git to work easily with that remote. Your typical day will look something like this.
- Create and 'checkout' a local branch named 'feature-1' from the 'master' branch to work on a feature.
This is a local feature branch that's not replicated in the remote.
- Make a small set of changes to the files.
Addthe changes to the index.Committhose changes with a short message- Do this a bunch of times until the feature--or enough of the feature to make available to everyone--is complete (tests run, etc).
- Interactively
rebasethose commits, combining them and updating the messages so the changes will be clear in the remote repository history that will be shared with everyone. Checkoutthemasterbranch- Pull (fetch and merge) any changes from the remote's
masterbranch into your localmasterbranch. - Checkout the
feature-1branch. Rebaseonto themasterbranch. This makes it seem as if all your changes are also the latest changes.- Checkout
master - Merge
feature-1intomaster Pushyour localmasterbranch to the remotemasterbranch.- Delete your local feature branch
- Create and
checkouta new feature branch and do the whole thing again.
While this is many discreet steps, the flow soon becomes natural, and the result is a history of changes that's easy to follow.
Here are the commands for the above flow, which are explained in the Common Operations section.
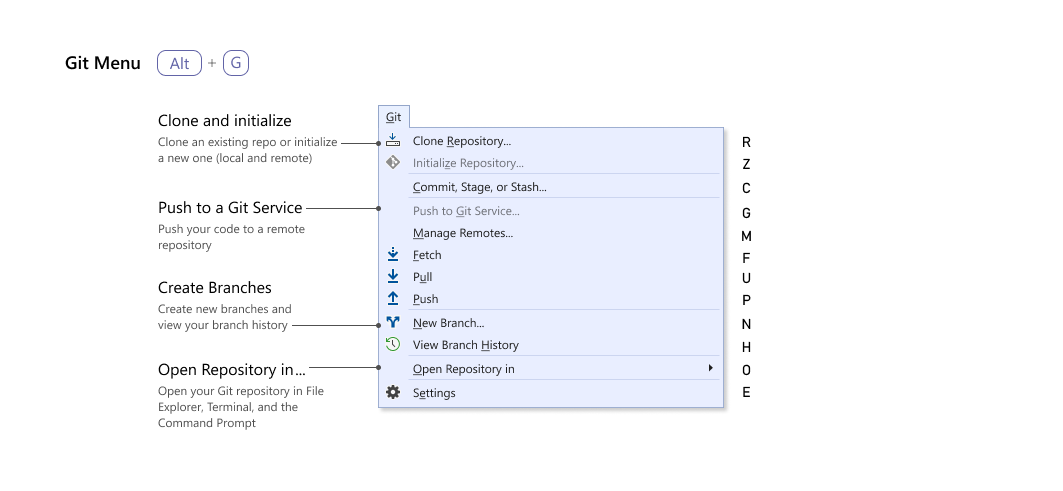
Doing It In Visual Studio 2019
Here are the same operations from above done in Visual Studio 2019. Using Visual Studio 2017 is very similar.
I don't recommend using Visual Studio 2015's Git features.
Create and Checkout a New Branch
git checkout -b feature-1
Stage Changes for Commit
git add -A
Note: In most cases you won't explicitly stage. You'll just Commit All.
Commit the Change
git commit -m 'Try use existing GetAddress feature for GetCustomer'
Make a Couple More Commits
git commit -m 'Update GetCustomer with new collectiongit commit -m 'Fix broken tests'
[Note shown]
Clean Up the Commits
git rebase -i master (result is a single commit with message 'Allow git GetCustomer to return addresses')

Note: Visual Studio only gives the option to 'squash' the commits. This is what you'll want to do most of the time, anyway.
Select the commits to squash, right-click, choose 'Squash commits...'
Note: Visual Studio's 'Squash Commits' dialog is surprisingly terrible. You effectively can't edit the text, because A) there's no way to create a soft return, and B) you can't paste more than the top line of copied text.
Until it's better, I recommend using the command line for squashing.
Checkout and Synchronize Master
git checkout mastergit pull
Checkout and Rebase Feature Onto Master
git checkout feature-1git rebase master
Checkout and Merge Feature Into Master
git checkout mastergit merge feature-1 --no-ff
Note: Visual Studio doesn't appear to have a --no-ff option. Because of the value to a good history, I recommend doing the final commit at the command line using an alias.
Note: It possible to set Git to always use --no-ff via the merge.ff false option. However, this will only work in your local instance unless a repository-specific config file is used and committed.
Here's how that commit looks after using --no-ff at the command line. Notice how much clearer it is in both the command window and Visual Studio
Push Changes to the Remote Server
git push
Delete the Branch
git branch -d feature-1
Common Operations
Checkout
Checkout means to set your working folder to a particular point in time. You're always choosing a reference hash of a 'root'. However, you can use branch and tag names because they 'point' to a particular reference.
Branch
With the above information about how Git works, you should now understand what people mean by 'a branch is a pointer to a reference.'
You may not use the branch command to create a branch very often. Typically, you'll create and checkout a branch in a single step using this command:
git checkout -b feature-1
That single command runs these two commands:
Other branch commands.
Add (stage)
Adds changes to the index, to be committed.
Commit
Commits staged changes (in the index) to the repository.
You'll often amend a commit if, for example, you realized you forgot to add a file, or mispelled something in the commit message.
For example, assume this history:
After committing 'Fix spelling erors', you realize you not only forgot to add the latest spelling file, but also mispelled 'errors.' You'd execute something like
The editor would open, and you could either change the message or--more likely--just close the editor. Here's how the result might look.
Here's the important thing to notice: The 'fix spelling errors' commit's ref hash has changed.
Merge
Merges changes from another branch into the current branch. You must have the destination branch checked out. For example, in order to merge the changes from the feature-1 branch into the master branch, you must first be in the master branch.
Rebase (changes history)
Rebase has two main uses. The first is to modify a set of commits, usually combining ('squashing') them, so that the resulting commits are 'the way it should have been'. For example, let's say you have these five commits in a local feature branch.
Using interactive rebase, you could revise this to two commits:
Notice that the original file reference hashes were not reused. New commits were created. It's as if these new commits had always been the only commits.
However, those other five commits still exist in the reflog if needed.
Here's the command:
The result is a screen that guides you through the changes.
The second use is making your branch's commits seem like they were just done so that they appear as the latest commits on another branch. For example, you're working on your feature branch and have cleaned up your commits. Now you want to merge your changes into master, so you checkout master and pull.
The problem is, while you were working, someone else committed changes to master. So now your changes are behind that other person's. If you were to merge your changes, then view history, they'd be kind of jumbled in. Instead, you want your changes to appear after the other person's.
To do that, you rebase your changes onto master. Git will temporarily reset your branch to when you originally branched, merge the latest changes from master into your branch (making them identical), then replay your commits on top of this history. Each of your commits is treated as new, so it gets a new reference hash.
The command sequence to do this is:
There's a chance you'll need to resolve conflicts between your changes and the other persons.
Check Status
Shows which files are modified, new, or deleted. Also shows which files are staged.
git status
Check History
Shows information about commits.
Revert
The revert command 'unapplies' a set of commits that appear after a commit in history, and creates a new commit at the top. Let's say you have this history.
Visual Studio Git Changes Window
Each commit that's reverted gets its own new commit. After each reversion, you need to enter git revert --continue until all reversions are complete.
Reset (changes history)
The reset command undoes a set of commits starting at the latest. It does not create a new commit. It effectively throws away the changes.
Basically, the HEAD file is updated to point to the given ref hash. In the example below, HEAD would change from 6293daae to bac6d253. The only other question is whether the commit changes are retained in some way.
Given this history,
Here are the common ways to use the command to remove the top three commits.
git reset bac6d253
The default command executes in --mixed mode. The index is reset, but the working folder is left alone. This means any changes are ready to add and commit.
git reset bac6d253 --soft
The index is not reset, nor is the working folder. Any changes are already added and ready to commit.
git reset bac6d253 --hard
Both the index and working folder are reset. All changes are lost.
Tag
There are two kinds of tags: annotated and lightweight. Annotated tags are meant for release (such as pushing to the remote repository), while lightweight tags are good for local use and cannot be pushed.
Personally, I only use annotated tags.
List all tags
git tag
Create a lightweight tag at the HEAD
git tag temp1
Create annotated tag at the HEAD, with a message of the same text
git tag -a v1.2.4 -m v1.2.4
Delete a tag
git tag -d v1.2.4
Force an existing tag onto a different commit
git tag -a -f 63fac95
The Rules For Teams
Git is powerful, and one of its powers comes with a risk. That is the power to 'rewrite history.' What this means in practice is that a user could push changes to a remote repository that conflict with existing log entries others have already pulled. I show an example below, but first here are the rules.
- Don't push changes from
rebase,revert,commit, ortagif you've previously pushed the affected commits. - Rebase features onto master, then merge features into master.
First, here's an example of an easy mistake to make. The user is on the master branch, commits locally, pushes to the remote, then amends the commit and pushes again.
Notice that the 'All done!' commit's reference hash is different after being amended. The problem above would be compounded if the user didn't amend the commit for awhile.
What if developer B pulls from the server after user A's first push? B will have a history that includes ref afea725. In the meantime, the A amends and pushes. Now B pulls. Does her ref afea725 magically disappear? No. She ends up with something like this.
Or, it could be worse. User A could force the amended commit. This will lead B to getting an even worse history.
Visual Studio 2019 Github Plugin
The problems arising from using the other commands that change history are similar.
Second, if a user doesn't rebase features onto master, then this leads to an unclear history where the branch the user just finished and is pushing to the remote server looks as if it was done a week ago (or whatever). That's because, according to the history, it has. But that's not what the user intended.
Solving Common Problems
Pull, Merge and Rebase Conflicts
The first time I encountered a merge conflict, I was utterly flummoxed. I didn't understand what to do, and I was definitely confused by whether my local files were actually 'local' or 'remote'.
Here's a message from trying to push changes that conflict with local changes.
So, we do what we're told and try to pull.
We're now in the midst of resolving a merge conflict. At this point we have two options: resolve the conflict, or abort. If we abort, it's as if the pull never happened.
To visually merge the files, click 'Conflicts: 1', then select a file that has a conflict.
There are several options for comparing and merging files. The one we'll look at is the three-way merge. Click Merge. This will run whatever merge tool you've configured Git to use.
I've used KDiff3 for years because it's very clear about where the conflict is. However, since this article is about using Visual Studio, that's what I'll demonstrate. It looks like Microsoft has improved Visual Studio's diff/merge quite a bit, which is good!
Choose which version you want to keep, the left or right or both. You can also type directly into the base. We'll take the left (our) change, Accept Merge, and close the editor.
Finally, commit the merge.
And, you're ready to push.
Remote vs Local, plus Base and Backup
The 'base' file is easy to understand; it's the version that's common to both of the changed versions prior to when they diverged.
If you're dealing with a merge conflict from another developer, that's easy, too. The Remote will be their file, and Local will be yours.
But what if there's a conflict locally between two branches? For example, what if you
Visual Studio 2019 Github Ssh
- Branch from master into feature, commit a change there
- Go back to master and commit a change there
- Try to merge feature into master OR rebase feature onto master
Visual Studio makes this pretty easy by using clearer terminology.
In the case of Merge, the master branch file is the Target, and the feature file is the Source. If you used the command git mergetool, master would be LOCAL and feature would be REMOTE.
In the case of Rebase, it's the same: 'masteris Target/LOCAL, andfeature` is Source/REMOTE.
Merge vs Rebase terminology is what confuses people, so let's repeat it:
- If I'm on
masterbranch and merge,masteris Target/LOCAL - If I'm on
featurebranch and rebase,masteris still Target/LOCAL
The target is whichever branch you're merging into, or rebasing onto.
If Git is configured to keep backups of the file before merging begins (mergetool.keepBackup = true), after the merge is committed there will be files with a .backup extension. These need to be cleaned up.
git clean -f
I suggest setting the config file's mergetool.keepBackup to false. Several times I've accidentally added the backup files to a commit.
Last Word
Git's powerful, at times confusing, always complex, and frequently complicated. Hopefully this article has given you a solid foundation in Git's basics.
